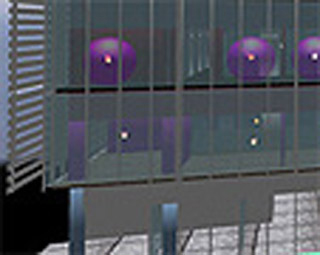
A sensor visualization of MIT's Media Lab complex rendered by the DoppelLab project in Prof. Paradiso's Responsive Environments group. DoppelLab uses the popular game engine Unity3D to transform architectural models into a browsing environment for real-time sensor data visualizations, as well as an open-ended platform for building visual applications atop those data. (Image by Prof. Joseph Paradiso.)
Instructor(s)
Prof. Joseph Paradiso
MIT Course Number
MAS.836
As Taught In
Spring 2011
Level
Graduate
Course Description
Course Features
Course Description
This course is a broad introduction to a host of sensor technologies, illustrated by applications drawn from human-computer interfaces and ubiquitous computing. After extensively reviewing electronics for sensor signal conditioning, the lectures cover the principles and operation of a variety of sensor architectures and modalities, including pressure, strain, displacement, proximity, thermal, electric and magnetic field, optical, acoustic, RF, inertial, and bioelectric. Simple sensor processing algorithms and wired and wireless network standards are also discussed. Students are required to complete written assignments, a set of laboratories, and a final project.
Other Versions
Other OCW Versions
Archived versions: ![]()